Hi 5! The five fintech stories we’re following this week
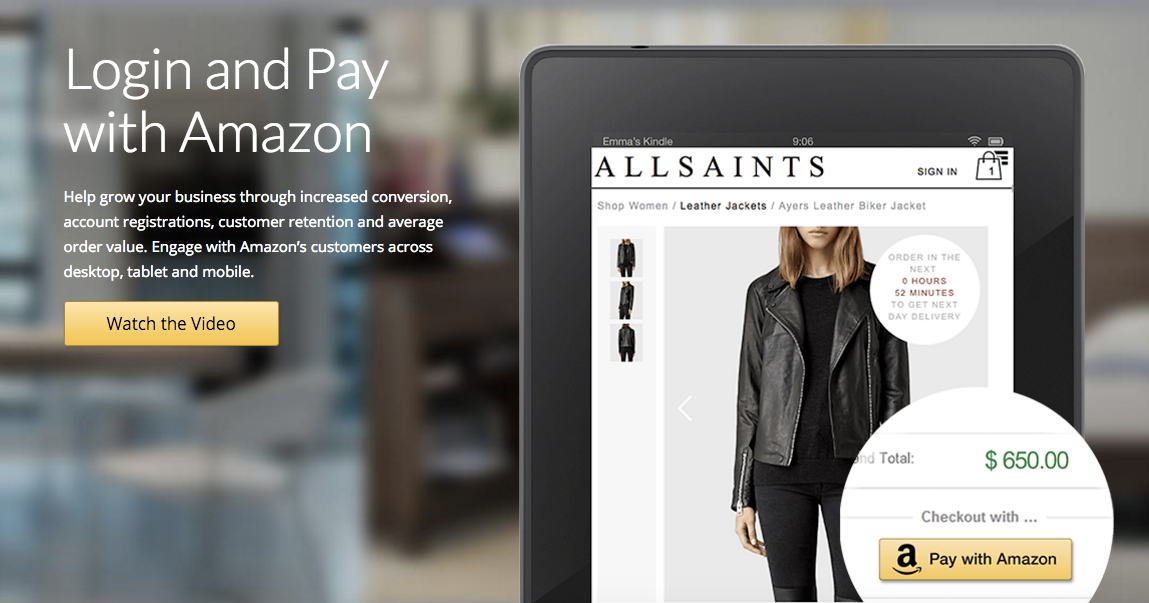
How Amazon is becoming a major player in finance
Invest In Small Businesses With An Ecommerce Twist — Kickfurther’s Sean De Clercq
Many people have grown tired of passive investing. Sure, the data show that the more remove the human elements — our evolutionary biases — the better we perform in the stock market.
But many investors are getting more and more excited about participating more with their investments (I believe that’s what’s behind much of the excitement behind angel investing).
Enter Kickfurther. Part investment platform, part crowdfunding platform, and part ecommerce site, this new company enables people to finance small businesses and earn an equity-like return. I’m Zack Miller, your host on Tradestreaming Radio, and I’m joined by Sean De Clercq, Kickfurther’s founder and CEO to discuss how investors are rolling-up their sleeves and helping the next generation of small businesses grow.
Listen to the FULL episode
About Sean
 Sean is the founder and CEO of Kickfuther.
Sean is the founder and CEO of Kickfuther.
Resources mentioned in the podcast
- Kickfurther (Sean’s company)
- Sean recommended listeners read The Richest Man in Babylon (Amazon link), a book he found that establishes the framework for becoming rich through investing as an ongoing process. I agree. Check it out.
Even more resources
Photo credit: JeepersMedia / Visual hunt / CC BY
Why I wouldn’t want to be a bank in this market
 As the late Rodney Dangerfield put it so eloquently, banks don’t get no respect in today’s market.
As the late Rodney Dangerfield put it so eloquently, banks don’t get no respect in today’s market.
It’s not that they haven’t tried. Post the 2007-2008 credit crisis, many of them have cleaned up their acts.
- they’ve stopped predatory lending (well, kinda)
- they’ve shored up their capital reserves (actually, they have to add another $68 billion against future financial disasters)
- they’ve shut down underperforming branches (truth is, they can’t close ’em fast enough)
But, it’s not just the fact that banks are now forces to lay in their own financial beds that has made bankers lives so tough of late.
Banks face (new) tough competition
It’s also about competition. Banks are being assailed on all fronts in a way they’ve never been threatened and I think the writing is one the wall: the core functions of banking are being challenged by a whole new generation of startup financial service providers that may eventually displace them. We’re in the early stages of sprinting a marathon to build the most influential finance companies.
Today’s consumer lending: from the consumer to the consumer
One of retail banking’s bread and butter business lines is a basic form of lending arbitrage. They take deposits from customers (paying out a low interest rate) and then lend it out to other customers (at a higher interest rate).
But many individuals are borrowing outside traditional banking channels. Lending Club, the largest peer to peer lender, just surpassed $4 billion in small personal loans it’s underwritten on its platform. Borrowers on peer to peer lending platforms either couldn’t qualify for loans, got worse rates with banks or just would rather avoid the banking sector all together. Banks see the writing on the wall — Union Bank just announced it would team up with Lending Club to deploy its own capital into loans on Lending Club’s website. You can hear how far the company has come since my 2012 interview with Lending Club founder and CEO.
Business loans: the next domino to fall
Lending Club made it very clear as it gears up for its own multi-billion dollar IPO (expected this year) that it’s interested in getting into business loans. It’s here, in the commercial loan business, that banks are facing their fiercest rivals right now.
- Long term loans: Newly-minted companies like Funding Circle has already lent out hundreds of millions of dollars to business looking to borrow money for years at a time. The demand for these types of loans from non-banking sources is huge.
- Short term loans: Businesses looking for shorter term loans and access to working capital are turning more and more to companies like OnDeck. Armed with new credit models, these firms can frequently be more quick and nimble, approving loans in minutes (versus days and weeks at traditional lenders).
- Specialty loans: Perhaps the most interesting entrants into the online lending market are the specialty ecommerce and payment platforms. Amazon is hiring boatloads of people to staff up its new lending division. Paypal is doing the same with its new Working Capital loans for small businesses that use the payment platform. These companies are perfectly situated in their customers’ business to a) determine creditworthiness and b) to provide them with a loan. And student loans? Forget about it — there are startups like Pave (hear my recent interview with Pave’s co-founder) trying to create more efficient (and cheaper) ways to finance higher education.
Look for more innovative online lending models to proliferate in the next few years like the kind that Zazma employs. A startup that’s received investments from top venture capital firms, Zazma provides trade financing to small businesses. Need to stock up on some inventory before the holiday season? Zazma will pay your supplier for the goods and work with you on payback — all almost instantly online. Low friction like credit cards and quick access to working capital.
Today’s “no respect” for the banking sector is so much more than just the product of the recent credit crisis. Smart, well-funded startups are beginning to chip away at banks’ core value to the economy and consumers (both retail and business) seem to happier with their new-found options.
What do you think about the changes in the lending market? Let’s discuss in the comments below.
Groupon-like buying opens up new investable markets
This is a far-fetched idea but run with it a bit. We’re already seeing the creation of secondary markets in groupon deals. These are eBay-like exchanges like Lifesta where customers who bought a coupon can sell it to someone else looking for access to that particular deal.
Taking this further, what would happen to these secondary market if they matured? They could potentially morph into real-time exchanges, like the stock market, where customers call transact with one another but more interestingly, vendors (supply-side) can essentially bid on where a particular customer will dine on a particular night (demand). Supply and demand meet and prices determined in real-time. It could allow small businesses to manage their yield, selling excess inventory at a discount to recoup costs.
Anyway, the idea wasn’t mine but it got me thinking about it. Matthew Ingram on GigaOM discussed this in a post on the future of local social buying:
Right now, Groupon-style group buying is more or less just coupons that get sent to you via email to entice you to sign up. What if you could look at a real-time, auction-style exchange of local offers from merchants or retailers or restaurants in your vicinity — maybe even on your mobile device — and pick the offer you wanted for dinner that evening? You can’t do that now, but that’s one vision of where the local group-buying phenomenon is headed in the future, according to Don Rainey, a partner with Grotech Ventures and an investor in LivingSocial, the number two player in the U.S. group-buying market next to Groupon.
Rainey said he sees a day when merchants and potential customers interact through a kind of real-time exchange — like a stock exchange, with buyers and sellers, but for local offers on meals or other goods. “I can see local retailers and consumers bidding in a real-time system for where that consumer is going to go for dinner,” says Rainey. If a merchant is having a slow night, they can put an offer into the system and users can choose between that and multiple other offers, based on location and the time they want to go out. As someone who is constantly looking for new options for places to eat in my local area, this sounds like a winner to me.
Local deals become an investable asset of sorts. Investors could speculate on in-demand seats at swanky restaurants finding liquidity in these platforms (whether they profit or not). Fixed supply (like art) and fluctuating demand could influence big rises and falls in the prices of these assets.
Like I said, far-fetched but interesting to think about.
Source: LivingSocial and the Future of Local Group Buying (GigaOM)